Navigation
The navigation section of the content describes the path the user goes through as they progress. In simple terms, this can be thought of as a set of finite state machines, and the user progresses through each state until they hit a DONE node.
The navigation object contains a BEGIN property that contains a reference to a flow to start Player with. Once an end state is reached for that flow, Player will end its processing and return that outcome.
Flows are a state machine with 1 start state and at least 1 end state. The nodes are processed in order until an end state is reached. The flow that initiated Player (the BEGIN reference) will be executed until its END state is reached.
Flows can also contain an onStart or onEnd property which is an expression that will be evaluated before processing of the first start state takes place, or just prior to ending the flow.
Navigation State Types
Section titled “Navigation State Types”There are a few main navigation state types defined. Each has a slightly different interaction with how it progresses to the end.
All state types (except the END node) contain a transitions property. This is an object describing the relationship on how to proceed to the next node. The key is the name of the transition that is performed, the value is the name of the state to transition to. A key of * can be used as a fallback for any transition value given that doesn’t match a pre-defined one.
The view node is the simplest and most widely used. It supports transitions and contains a ref property that corresponds with an id of the view in the views array.
{ "state_type": "VIEW", "ref": "view-1", "transitions": { "next": "VIEW_2" }}ACTION
Section titled “ACTION”An action node allows users to evaluate one of more expressions before proceeding to the next node. The value of the expression (the last value is used if the expression is an array), as the transition value to the next node:
{ "state_type": "ACTION", "exp": ["{{foo.value}} = 1 + 2", "{{foo.value}} > 0"], "transitions": { "true": "VIEW_1", "false": "VIEW_2" }}ASYNC_ACTION Experimental
Section titled “ASYNC_ACTION ”Similar to an ACTION node, this node allows for the use of the internal await function to await the execution of an asynchronous function. The state also has a top level await property for if the expression as a whole should be awaited.
{ "state_type": "ASYNC_ACTION", "exp": "conditional(await(someAsyncFunction()), true, false)", "transitions": { "true": "VIEW_1", "false": "VIEW_2", }, "await": true,},The end state represents a completion of a flow. It contains an optional outcome property that can describe the circumstance for ending the flow. No transition state exists as this marks the completion of the flow.
{ "state_type": "END", "outcome": "Done_FWD"}EXTERNAL
Section titled “EXTERNAL”The external state represents a state that can’t be resolved by Player itself — it defers resolution of the transition value to the application. This is typically used in conjunction with the ExternalActionPlugin in order to wire up the proper handler that can process these values.
Similar to the view node, external states contain a ref to describe the external state type:
{ "state_type": "EXTERNAL", "ref": "custom-state", "transitions": { "next": "VIEW_2" }}Player will remain in this state until the external handler responds with a transition value to move the current state in the state machine.
The flow state executes the referenced flow, and its outcome determines the transition to use.
{ "state_type": "FLOW", "ref": "FLOW-2", "transitions": { "next": "VIEW_2" }}Reaching this state will execute the FLOW_2 flow — and if FLOW_2 reaches an END state with an outcome of next, will transition to the VIEW_2 state
Expressions
Section titled “Expressions”State types can also contain onStart and onEnd properties for evaluating expressions. Order of operations:
onStart- Evaluated at the start of a node’s lifecycle; useful for updating data before it’s resolvedexponEnd- Evaluated last, right before transition.- For an
onEndexpression defined on an individual state, if a transition is halted (by validation or otherwise), theonEndexpressions for that state won’t be executed. - As Player’s navigation is a state machine,
onEndexpressions defined for the entire flow will only execute when the state machine ends the flow, by reaching anENDstate. Terminating the flow by unmounting Player (on any given platform) will not execute flow definedonEndexpressions as it would not have reached anENDstate.
- For an
Examples
Section titled “Examples”Single Flow
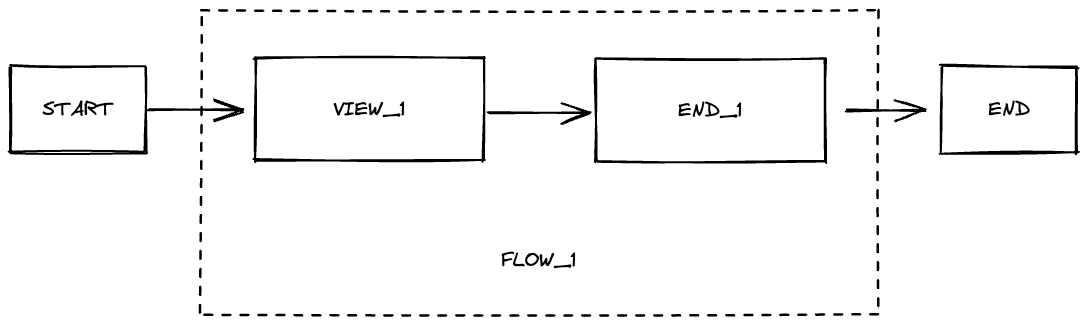
Section titled “Single Flow”{ "BEGIN": "FLOW_1", "FLOW_1": { "startState": "VIEW_1", "VIEW_1": { "state_type": "VIEW", "ref": "view-1", "transitions": { "*": "END_1" } }, "END_1": { "state_type": "END", "outcome": "Done" } }}This is the simplest of flows. The navigation begins with executing FLOW_1. FLOW_1 begins with the VIEW_1 state. VIEW_1 shows the view with id view-1, and any transition from that view goes to END_1 which completes Player’s execution with the Done outcome.
Flow with onStart expression on a VIEW state
Section titled “Flow with onStart expression on a VIEW state”{ "BEGIN": "FLOW_1", "FLOW_1": { "startState": "VIEW_1", "VIEW_1": { "state_type": "VIEW", "ref": "{{dynamicRef}}", "onStart": "{{dynamicRef}} = 'view-1'", "transitions": { "*": "END_1" } }, "END_1": { "state_type": "END", "outcome": "Done" } }}The view node in this flow utilizes an onStart expression to update the ref property dynamically. The expression is evaluated before the data is resolved, and the node references the updated id.
Flow with multiple expression types on a VIEW state
Section titled “Flow with multiple expression types on a VIEW state”{ "BEGIN": "FLOW_1", "FLOW_1": { "startState": "VIEW_1", "VIEW_1": { "state_type": "VIEW", "ref": "view-1", "onStart": "{{nextState}} = 'VIEW_2'", "exp": "{{nextState}} = 'VIEW_3'", "onEnd": "{{nextState}} = 'END_1'", "transitions": { "*": "{{nextState}}" } }, "VIEW_2": { "state_type": "VIEW", "ref": "view-2", "transitions": { "*": "END_1" } }, "VIEW_3": { "state_type": "VIEW", "ref": "view-3", "transitions": { "*": "END_1" } }, "END_1": { "state_type": "END", "outcome": "Done" } }}This flow demonstrates the order of operations for multiple expressions. On transition to VIEW_1 the onStart property’s expression is evaluated first, updating nextState to VIEW_2, followed by the exp updating it to VIEW_3. Right before the next transition the onEnd expression is evaluated; the flow transitions to the END_1 node.

